I previously introduced the concept of chirality and how it is a property of any molecule with only 1 stereogenic centre. (A molecule with  stereogenic centres may or may not be chiral, depending on its stereochemistry.) I also defined 2 stereoisomers as enantiomers if they are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. (Recall that chirality in inorganic chemistry can arise in 2 different ways.)
stereogenic centres may or may not be chiral, depending on its stereochemistry.) I also defined 2 stereoisomers as enantiomers if they are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. (Recall that chirality in inorganic chemistry can arise in 2 different ways.)
It is possible for 2 stereoisomers to NOT be enantiomers; in fact, such stereoisomers are called diastereomers. Yes, I recognize that defining something as the negation of something else is unusual. If you have learned set theory or probability (as I did in my mathematical statistics classes) then consider the set of all pairs of the stereoisomers of one compound – this is the sample space. The enantiomers form a set within this sample space, and the diastereomers are the complement of the enantiomers.
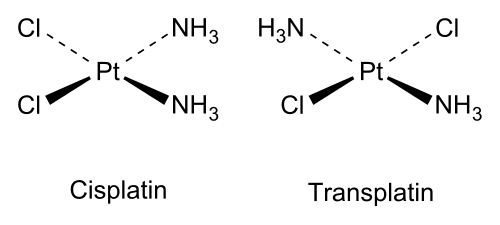
It is important to note that, while diastereomers are not mirror images of each other, they are still non-superimposable. Diastereomers often (but not always) arise from stereoisomers with 2 or more stereogenic centres; here is an example of how they can arise. (A pair of cis/trans-isomers are also diastereomers, despite not having any stereogenic centres.)
1) Consider a stereoisomer with 2 tetrahedral stereogenic centres and no meso isomers*. This isomer has  stereoisomers, where
stereoisomers, where  denotes the number of stereogenic centres.
denotes the number of stereogenic centres.
2) Find one pair of enantiomers based on one of the stereogenic centres.
3) Find the other pair enantiomers based on the other stereogenic centre.
4) Take any one molecule from Step #2 and any one molecule from Step #3. These cannot be mirror images of each other. (One molecule cannot have 2 different mirror images of itself.) These 2 molecules are diastereomers.
Think back to my above description of enantiomers as a proper subset within the sample space of the pairs of one set of stereoisomers. You can now see why I emphasized that the sample space consists of pairs, since multiple different pairs of stereoisomers can form enantiomers. In my example above, Steps #2 and #3 produced 2 subsets of enantiomers. It should be clear by now that enantiomers and diastereomers are defined as pairs. To further illustrate this point,
a) call the 2 molecules in Step#2 A and B.
b) call the 2 molecules in Step #3 C and D.
A and B are enantiomers. A and C are diastereomers. Thus, it is entirely possible for one molecule to be an enantiomer with a second molecule and a diastereomer with a third molecule.
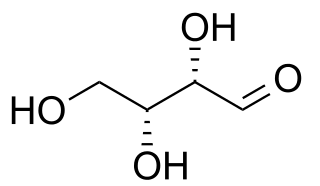
Here is an example of 2 diastereomers. Notice that they have the same chemical formula but different 3-dimensional orientations – i.e. they are stereoisomers. These stereoisomers are not mirror images of each other, but they are non-superimposable – i.e. they are diastereomers.

(-)-Threose

(-)-Erythrose
Images courtesy of Popnose, DMacks and Edgar181 on Wikimedia. For brevity, I direct you to the Wikipedia entry for diastereomers showing these 4 images in one panel.
In a later Chemistry Lesson of the Day on optical rotation (a.k.a. optical activity), I will explain what the (-) symbol means in the names of those 2 diastereomers.
*I will discuss meso isomers in a separate lesson.

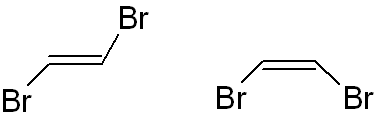



Recent Comments